Step 14: Avoiding Google Penalties

How can you avoid Google penalties and protect your website’s SEO visibility? This topic is vital because a search engine penalty can reduce or even wipe out your search traffic — and it can be costly and difficult to recover.
With every new algorithm update, Google seems to tighten its standards a little more and catch more websites operating just outside search engine guidelines. If your site is penalized, you can expect your rankings to slip and revenues to fall.
In this SEO tutorial step, you learn:
• What is a Google penalty
• Top 3 guidelines for avoiding Google penalties
• Google penalties by name
• Manual actions
What Is a Google Penalty
From an SEO perspective, the term “penalty” means any negative impact on a website’s organic search rankings caused by an algorithm update or a manual action.
Anything that directly violates Google’s Webmaster Guidelines can result in a penalty against your website. The two main types are algorithm-based, which is automatic, and manual, which is an intentional penalization for “black hat” actions.
Though Google doesn’t call algorithmic hits “penalties” per se, the end result feels the same to a website owner. It’s as if somebody threw down a penalty flag against your site.
Top 3 Guidelines for Avoiding Google Penalties
You can take steps to minimize the factors that contribute to SEO penalties. Here’s the top 3 guidelines to avoid a penalty:
- Don’t buy links. Links passing SEO value to your site should look natural. Make sure a “nofollow” attribute is added to any paid links (such as ads) and stay away from link schemes.
- Don’t overuse keywords. Stuffing your content with exact repetitions of a key phrase can hurt your search engine rankings. Keywords are important, but use keywords appropriately in a natural-sounding way.
- Make original, quality content. You must have unique, high-quality web pages to rank.
Google Penalties by Name
Penalties range from a slight, temporary ranking hit (a slap on the wrist) all the way to expulsion from the search engine’s index.
Don’t let the cute black-and-white animals fool you. Search engine algorithms have teeth in them and can bite sites that seem to be breaking the rules.
Google Panda Penalty
The Panda update came into being February 2011 with the first of many rollouts. By early 2016, Panda had grown up and become part of Google’s core algorithm.
The Google Panda algorithm aims to prevent poor quality content from making it to the top of search results.
If Panda thinks your website provides low-quality content, it will be hard for your web pages to rank. Examples of low-quality web content include: “thin” pages with little or no added value; product pages with manufacturer-provided descriptions and no original text; and widespread duplicate content.
(The SEM Post’s guide to Google Panda is a good resource for more details.)
How to Avoid a Panda Penalty: Keep Panda fed and happy by providing original content that will satisfy searchers.
With a Panda issue, you can earn your way back up the search results by fattening up (rewriting/improving) your thin content, eliminating duplicate pages (or blocking them from search engines), and generally providing high-quality content for your site visitors.
Google Penguin Penalty
The Google Penguin algorithm combats webspam by detecting link spam.
When a site’s backlink profile (i.e., the full list of links coming from external sites) includes too many unnatural-looking links, Google suspects that site of trying to manipulate search rankings — and Penguin’s feathers get understandably ruffled.
Google launched the first Penguin update in April 2012. Several agonizingly slow rollouts later, Google announced a final update in September 2016. Penguin now operates in real time as part of Google’s core ranking algorithm.
Google says that the new Penguin algorithm no longer gives penalties. Rather than demoting a site with low-quality backlinks, Penguin now just devalues bad incoming links so they don’t affect the site’s rankings.
However, your link profile is still your responsibility. Having a large percentage of poor backlinks is a low-trust signal. Many sites that were hit with a Penguin penalty still need to take steps to recover.
How to Avoid a Penguin or Link-Related Penalty: If Google detects a site is buying or selling links, negotiating link exchanges, participating in link farms, or engaging in any kind of unnatural linking, it should expect to get penalized.
Also, if your organic search traffic drops suddenly, it could be due to a link-related penalty. The traffic chart below shows a tragic but typical example:
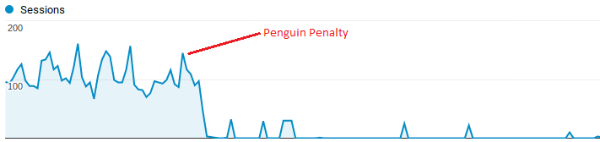
To avoid Penguin issues, regularly monitor and clean up your backlinks. (Stay tuned — you learn how to do this in the next lesson!)
Intrusive Interstitial Penalty
Launched in January 2017, the Intrusive Interstitial Penalty affects mobile search results only.
Google penalizes sites that show an intrusive ad, popup, or standalone interstitial to a mobile user immediately after clicking a mobile search result.
In general, Google demotes web pages that block searchers from easily seeing the content. Certain types of interstitials aren’t penalized, such as login forms and legally necessary gates (for age verification or other).
This image shows three examples (provided by Google) of intrusive interstitials that would cause a penalty:

How to Avoid an Interstitial Penalty: Give mobile searchers a good user experience. Avoid ads and popups that block too much of the screen right after a searcher arrives.

Photo by Jason Comely (CC BY 2.0), modified
Payday Loan Penalty
Google updated its algorithm in June 2013 specifically to address the quality of results for heavily spammed queries such as “payday loans,” “viagra” and pornography-related keywords.
How to Avoid a Payday Loan Penalty: Sites penalized by the Payday Loan update tend to be heavily involved in link schemes, web spam, and often illegal activities. Steer clear of these, or you risk losing your organic search engine rankings.
This list covers Google’s major algorithmic penalties to this point. For a complete list of all the known updates, see Moz’s Google Algo Change History.
Manual Actions
Besides all of the algorithmic penalties, it’s also possible for a search engine employee to manually cause your website to go either up or down in the rankings. Google’s webspam team members can manually review websites and levy penalties or even kick a site out of the index.
What triggers a manual review? The search engine may be taking a closer look because of suspected foul play. (Did you know a majority of spam is reported by competitors?) Or, Google’s team may be re-evaluating a website that has requested “reconsideration” after cleaning up its penalty issues.
How to Check for Any Manual Actions: If your site receives a manual action notice, Google courteously tells you so. In fact, Google sent over 9 million webspam notifications to webmasters in 2016 alone.
Here’s how to see if any messages (good or bad) exist for your site:
- Log in to your account in Google Search Console.*
- Open the Manual Actions report.
- Read any messages to find out the specific reasons for the manual action and what parts of your site are affected by the penalty.
How to Avoid a Manual Action Penalty: Manual actions can result from anything that directly violates Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. They often relate to thin content (see Panda Penalty section), unnatural links (see Penguin Penalty), pure web spam (see Payday Loan Penalty), or other noncompliance issues.
If your site gets a manual penalty, resolve the issue(s) causing the manual action sooner rather than later.
Once you clean up your site, submit a reconsideration request. Google will examine your site again and, if it looks good, lift the penalty.
SEO TUTORIAL BONUS VIDEO
Google’s Gary Illyes explains how the Penguin algorithm works now that it’s a real-time component of the core ranking algorithm.
BONUS VIDEO #2
“How can you prepare for the future of SEO?” Bruce Clay addressed this question at a search conference, and his response was fortunately captured on video.
His advice — In the short term, monitor and get rid of “junk links.” Long term, reinforce your subject relevance through proper site structure. These strategies help you avoid Google Penguin penalties and other “disasters.”
Watch this brief interview to hear Bruce’s full answer.
Building on the important topic of avoiding Google penalties, the next step in the SEO tutorial shows you how to monitor your backlinks and remove unwanted links that could sink your SEO ship if a link penalty occurs.
Related blog posts and articles:
What a Website Can Do about Thin Content — 4 Common Scenarios and Solutions
Manual Penalty Actions Reported in Google Webmaster Tools
9 Tips for Getting Your Manual Link Penalty Overturned
3 Ways to Keep Google Panda Fed and Happy
Do you think you’ve been hit with Google penalties? We can help. Read about our SEO Penalty Assessment and optional link pruning services that can help businesses identify and recover from Google penalties.





