SMX East 2011: Hard Core Local SEO Tactics
Here’s another session revived as a favorite from SMX Advanced. However, since the last time these presenters spoke, lots has changed in the local search arena.
 |
Today’s speakers are Mike Ramsey (@niftymarketing), Matt McGee (@mattmcgee) and Will Scott (@w2scott).
We’re about 5 minutes into the session and I lost everything I’d typed. The joys of liveblogging! I’ll try to dive right in and also fill in lost info …
Okay, Mike Ramsey is presenting and he’s sharing findings from the Local Search Ranking Factors report.
The Local Search Ranking Factors report is an annual study you can find at DavidMihm.com. Thirty of the most prominent experts in local search share their opinions on local search factors.
It looks at integrated O-pack results and not 7 pack results. There are generally more integrated O-pack results in the wild. The study compares the results found at positions 1-7 and results found at positions 50-56. It seeks to identify correlations between high ranking and low ranking results.
Disclaimer: correlation does not equal causation.
Reviews
The more places you have reviews, the more places reviews come from, the greater a factor of location prominence you get.
Reviews are better for click-throughs instead of rankings. Generating clean, pure reviews, you’ll look real. That’s the most important thing for getting a customer to look at you. It’s not about quantity. It’s about trust signals.
Citations
This is anywhere the biz name, address and local phone number are (NAP). Citations are a very important ranking factor. Google used to show a base list of citations on a places page. As of the July 21 update, they removed citations. The average biz had 36 listed on a places page, and 24 on pages ranking low.
A custom search for citations is: “biz name” + “address” + “phone number”
The highest correlation in the whole study is citations. High ranking results had thousands of citations on average, while low ranking results had extremely few. The info on the company wasn’t out there and available.
Offsite data: High rank = 2058. Low rank = 242
Linking root domains: High rank = 157. Low rank = 25
If citations were the new links for local in 2009-10, links are the new citations for local in 2011-12.
Average domain authority and average page authority didn’t have as big an influence as he would have guessed.
3 main takeaways:
- Exactness in place: citations + categories + content
- Authority in website: quality of links
- Trust in reviews: CTR + UGC
At SMX Advanced in Seattle, David Mihm gave a detailed presentation. When David couldn’t make it today, Matt McGee decided to try to give his presentation for him. There will be a few things that are different when Matt gives his presentation.
What are your opportunities?
1. What phrases are you behind your competition organically?
2. When does the map/blended results show up?
You might get a 7-pack vs. an integrated organic pack from computer to computer, day-to-day, one word difference. Impossible to predict.
3. How many bizs are listed if it shows up?
Google Insights for Search lets you compare major metropolitain areas around the world to see “lawyer” vs. “laywers” in your area, for example.
Impact of Blended Results
How does blended local search work? Read the patent. It’s readable and understandable. The thing to understand is Google is trying to keep as much of the traffic for themselves as possible. A search for Nordstrom gives a searcher all the info a user needs to locate or contact a store without leaving the search results = pre-website conversion. A lot of activity happening for your business off of your website.
Pre-website conversion:
Localized inventory: displays if a product is in stock nearby
Proper Mindset: Understand that local requires a different mindset than general SEO.
The impact of blended results:
- The top spot is really important.
- Photos are very important.
- There’ve been a lot of studies on eyetracking on blended search results. Now our eye goes all over the place.
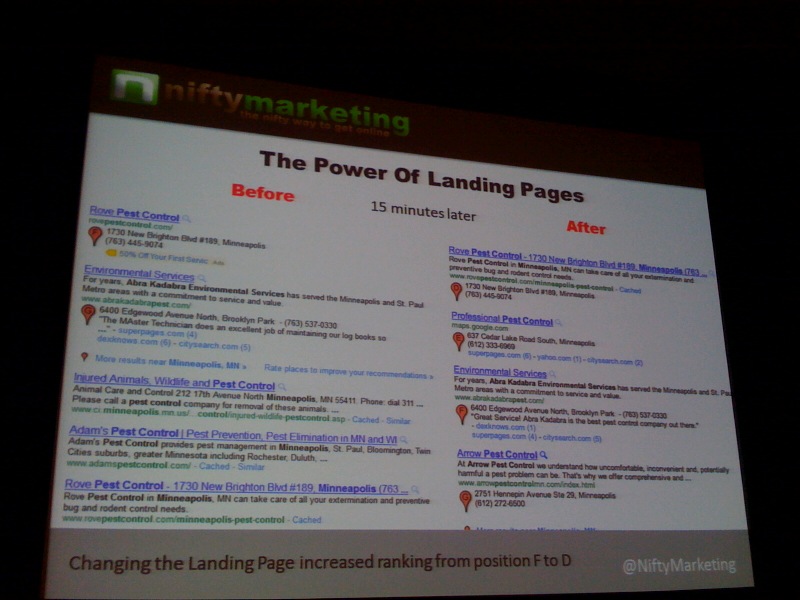
Fundamental best practice: submit your contact/location page as your Places URL/Landing page.
On-page stuff:
- Each location needs its own landing page.
- See Best Buy as an example of doing it right.
- KML site map to submit to Google where all your locations are.
Local landing pages are not that different than PPC landing pages – with one major exception. DO NOT USE TRACKING PHONE NUMBERS. ANYWHERE. EVEN OFFLINE. (Unless they are online only and appear as an image or un-indexable JavaScript. You don’t want Google to be less certain about where you are and where you can be reached.)
Off-site stuff:
- Citation priorities.
- CONSISTENCY: authority, vertically relevant, geographically relevant.
- Consider starting with the whitespark citation finder, but it’s no substitute for human analysis.
- Look for the sites where Google pulls citations from.
- Check the sites that rank well in organic results for your keywords.
- Look for high-authority/trust sites.
- Google is obfuscating Place Page citations more than ever.
- Search just on city name and go several pages deep – lots of interesting sites you may not know of.
The hard stuff: reviews:
- E-mail campaigns: segment customers with Gmail/Yahoo email addresses.
- Consider the ease of leaving a review for someone without an account.
- Consider the syndication value of review sources.
- Point of sale follow-up: feedback should be part of everyday biz process. Review velocity should be consistent.
- Caveats: know the rules for incentives, watch for review threshold.
What makes the difference in competitive markets?
- Get your bulk feed verified.
- Make sure Google Account email TLD matches Places TLD.
- Clean up and consolidate ole/duplicate listings.
- Geo inbound anchor text.
- Use custom categories for high-volume, high-conversion keywords.
- Strong industry relevant review volume.
- Order of magnitude “rule” (suburbs vs. downtown).
- Elite reviews.
Will Scott is presenting next. He’s going to talk about some really tactical things, and close with something that was also in the last 2 presentations. If you don’t leave this room and do it, thanks for giving him business.
The Tactics
Community Edits:
- The hard way
- Google’s new mapmaker
Alternative Citation Sources:
- Articles
- Other community sites
Do This Now:
- Take a NAP
- Geo title
Wait, That’s Not Me: Doing community edits over and over the course of months may eventually wipe out the bad info. You also need to chase down the source of the bad info and kill it, too.
Google MapMaker isn’t as important as community edits.
MapMaker Tips
- The more explanation/reasons you give for why you want your edit to be approved, the better.
- Be truthful/honest telling them why you want the edit and give backup.
- Even give links, etc. Do all the work for the editor so he can say “approve!” more easily and quickly.
Alternative Citation Sources: Facebook, foursquare, Yelp, Gowalla – anywhere with social and local signals.
All the World’s a Citation: it’s really simple. If it has your NAP as Google understands it and it’s near a link to your site, it’s a citation. Get them all.
26,000+ professionals, marketers and SEOs read the Bruce Clay Blog
Subscribe now for free to get:
- Expert SEO insights from the "Father of SEO."
- Proven SEO strategies to optimize website performance.
- SEO advice to earn more website traffic, higher search ranking and increased revenue.

4 Replies to “SMX East 2011: Hard Core Local SEO Tactics”
@Virginia….nice recap here! thanks….on behalf of those of us who couldn’t make it to the conference….great read!
:-)
Jim
LEAVE A REPLY